21
2025-01
Astronauts Set to Swab the Exterior of Station for Microbial Life
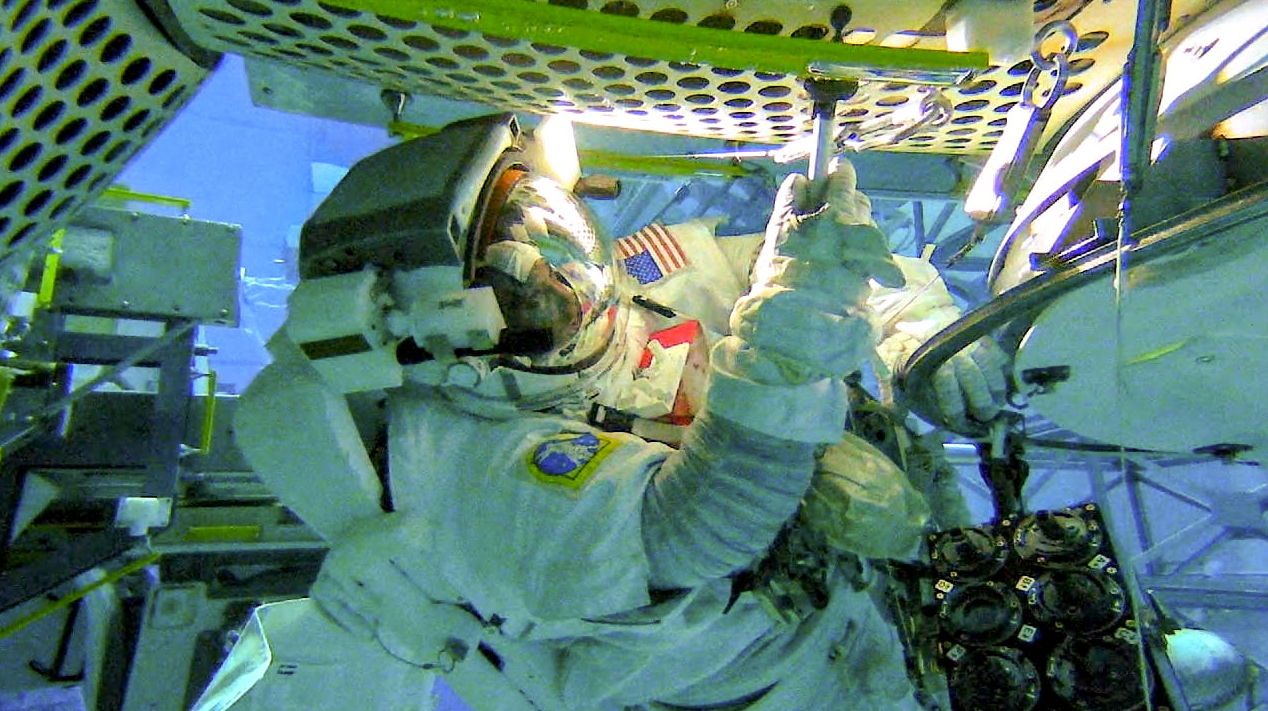

Astronauts are scheduled to venture outside the International Space Station to collect microbiological samples during crew spacewalks for the ISS External Microorganisms experiment. This investigation focuses on sampling at sites near life support system vents to examine whether the spacecraft releases microorganisms, how many, and how far they may travel.
This experiment could help researchers understand whether and how these microorganisms survive and reproduce in the harsh space environment and how they may perform at planetary destinations such as the Moon and Mars. Extremophiles, or microorganisms that can survive harsh environments, are also of interest to industries on Earth such as pharmaceuticals and agriculture.
Spacecrafts and spacesuits are thoroughly sterilized before missions; however, humans carry their own microbiomes and continuously regenerate microbial communities. It’s important to understand and address how well current designs and processes prevent or limit the spread of human contamination. The data could help determine whether changes are needed to crewed spacecraft, including spacesuits, that are used to explore destinations where life may exist now or in the past.
Source: nasa.gov
-
29
2025-05
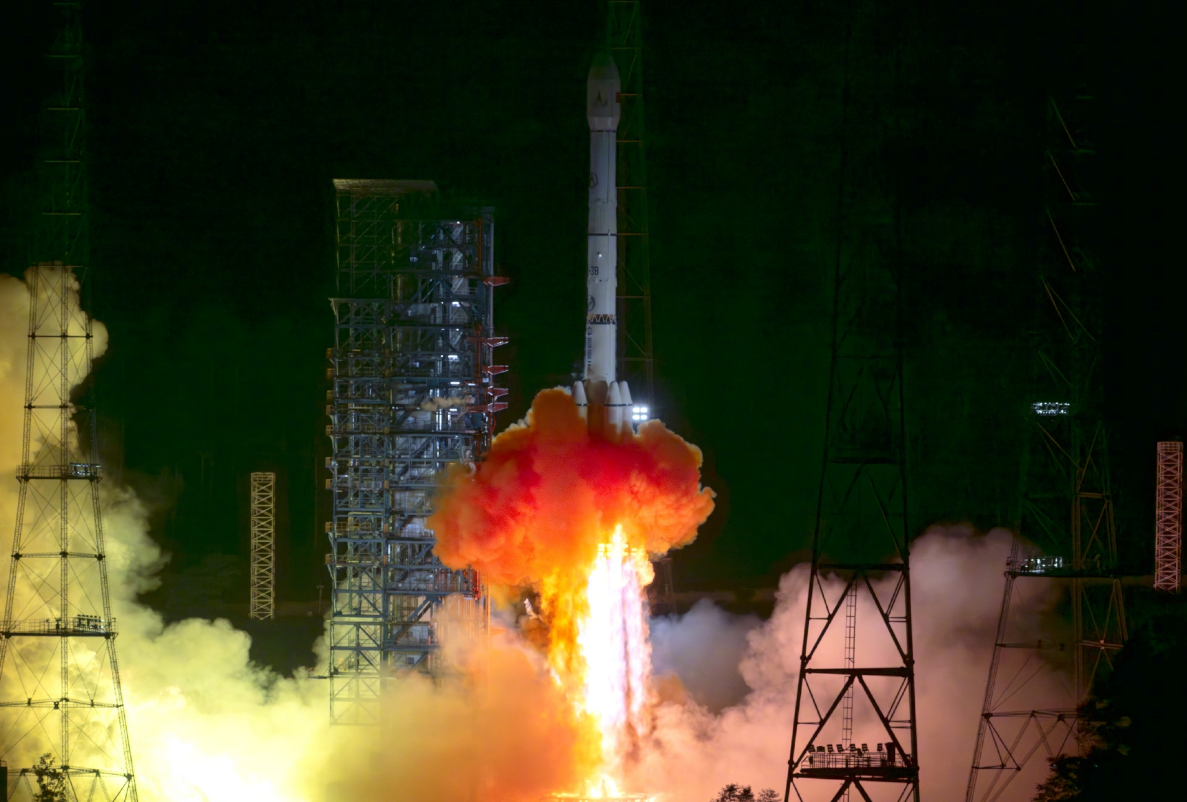

Tianwen-2 Mission Launched Successfully
At 1:31 AM today, China successfully launched the Tianwen-2 planetary exploration probe from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center using the Long March-3B Y110 carrier rocket.
-
13
2025-05
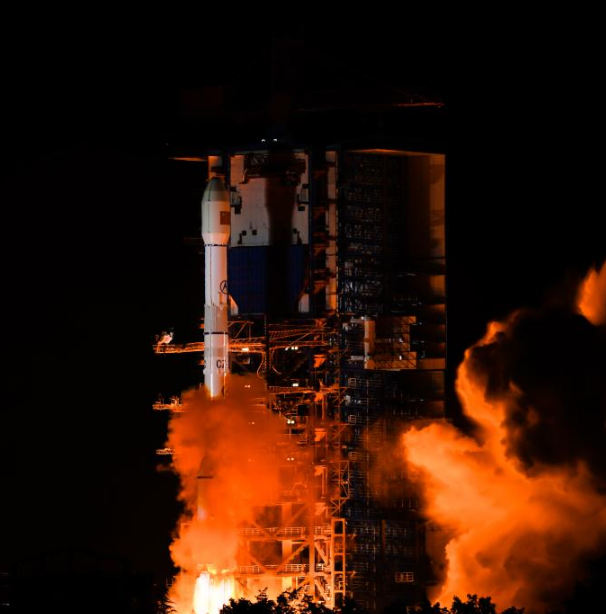

Communication Technology Experiment Satellite No. 19 Successfully Launched
At 2:09 on May 13, China successfully launched the Communication Technology Experiment Satellite No. 19 from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center using a Long March 3B carrier rocket. The satellite smoothly entered its predetermined orbit, and the launch mission was a complete success.
-
12
2025-05
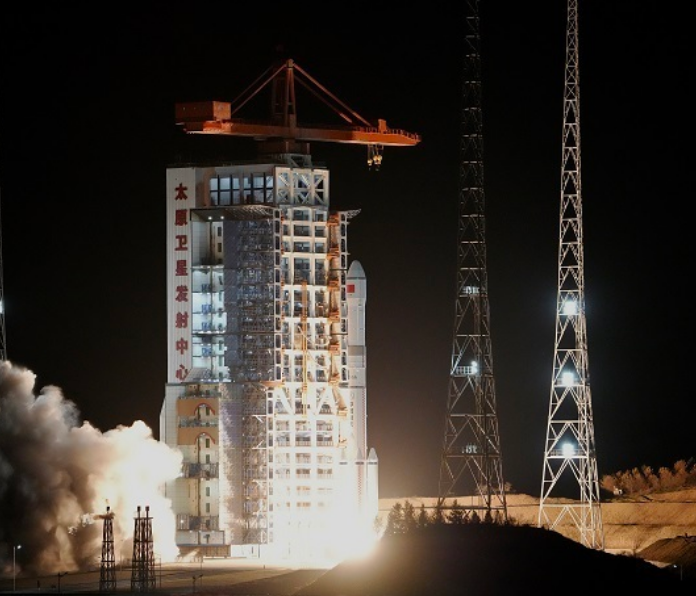

Remote Sensing Satellite No. 40, Group 02, Successfully Launched
On May 11 at 21:27, China successfully launched the Remote Sensing Satellite No. 40, Group 02, from the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center using a Long March 6A carrier rocket. The satellite entered its predetermined orbit smoothly, and the launch mission was a complete success.